What to except during a 9 Month Old Physical?
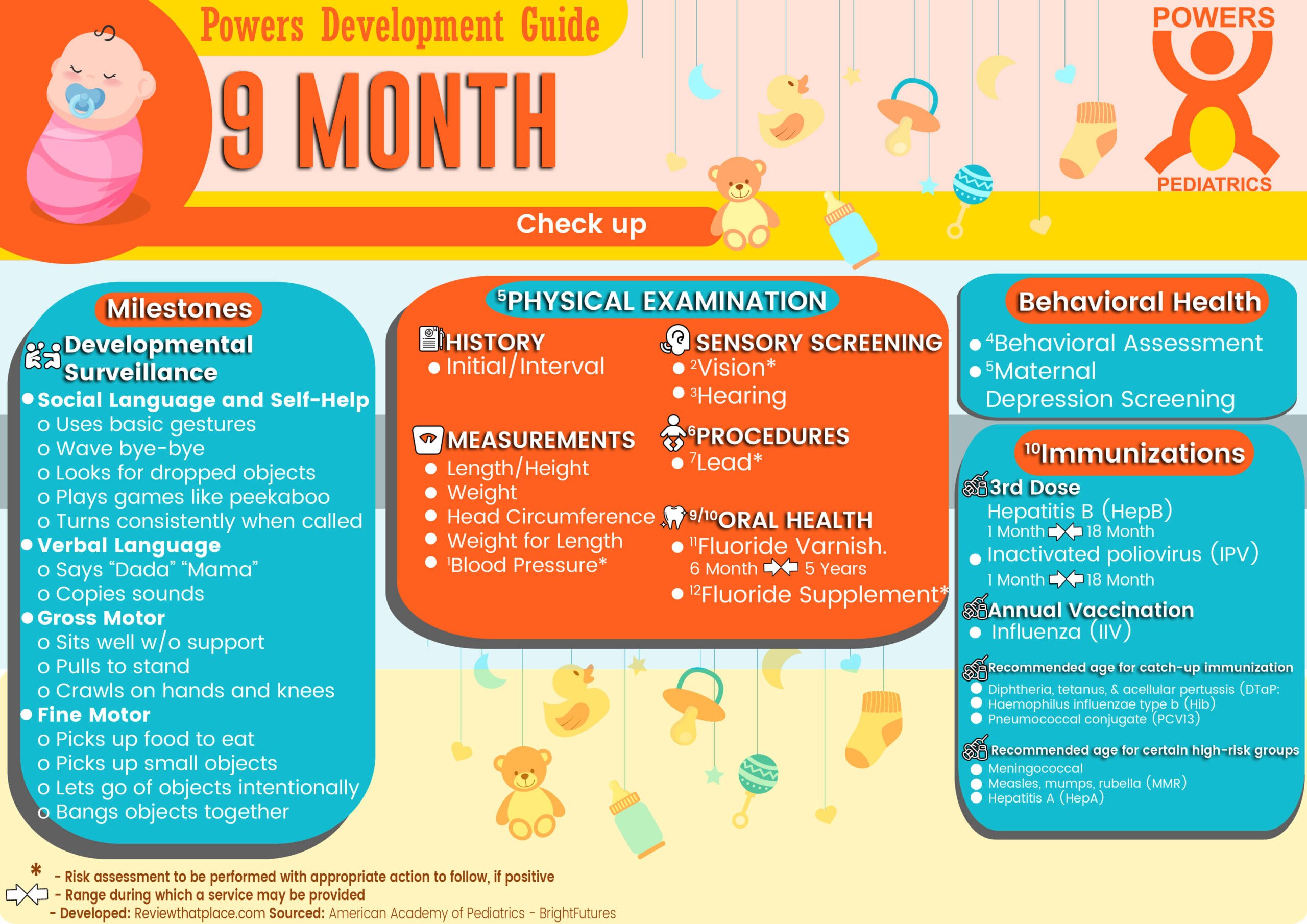
DEVELOPMENTAL SURVEILLANCE
- Social Language and Self-Help
- Uses basic gestures
- Wave bye-bye
- Looks for dropped objects
- Plays games like peekaboo
- Turns consistently when called
- Verbal Language
- Says “Dada” “Mama”
- Copies sounds
- Gross Motor
- Sits well w/o support
- Pulls to stand
- Crawls on hands and knees
- Fine Motor
- Picks up food to eat
- Picks up small objects
- Lets go of objects intentionally
- Bangs objects together
BEHAVIORAL HEALTH
3 PHYSICAL EXAMINATION
- History
- Initial/Interval
- Measurements
- Length/Height and Weight
- Head Circumference
- Weight for Length
- 4 Blood Pressure*
- Sensory Screening
- 5 Vision*
- Hearing*
- Procedures
- These may be modified, depending on entry point into schedule and individual need.
- 6 Lead*
- 7 8 Oral Health
11 Immunization
- Recommended age for catch-up immunization
- Diphtheria, tetanus, & acellular pertussis (DTaP:
- Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib)
- Pneumococcal conjugate (PCV13)
- Recommended age for certain high-risk groups
- Measles, mumps, rubella (MMR)
- Hepatitis A (HepA)
- Meningococcal (MenACWY-D ≥9 mos; MenACWY-CRM ≥2 mos)
- 3rd Dose Hepatitis B (HepB)
- 1 Month – 9 Month – 12 Month – 15 Month – 18 Month
- 3rd Inactivated poliovirus (IPV: <18 yrs)
- 1 Month – 9 Month – 12 Month – 15 Month – 18 Month
- Influenza (IIV)
- Annual vaccination 1 or 2 doses
range during which a service may be provided
* risk assessment to be performed with appropriate action to follow, if positive
9 Month Old Anticipatory Guidance
Social Determinants of Health
◊ Risks (intimate partner violence)
◊ Strengths and Protective Factors (family relationships and support)
- Do you always feel safe in your home? Has your partner ever hit, kicked, or shoved you, or physically hurt you or the baby? Would you like information on where to go or who to contact if you ever need help?
- Ask for help if you are concerned about or have experienced violence from your partner or another significant person in your life.
- You can also call the National Domestic Violence Hotline toll-free at 800-799-SAFE (7233).
- Make time for self, partner; maintain social contacts.
Infant behavior and development
◊ Changing Sleep Pattern (sleep schedule)
◊ Developmental Mobility
◊ Cognitive Development
◊ Interactive Learning
◊ Communication Media
- Keep consistent daily routines.
- Provide opportunities for safe exploration; be realistic about abilities.
- How does your baby adapt to new situations, people, places?
- Recognize new social skills, separation anxiety; be sensitive to temperament.
- How do you think baby is learning? How is he communicating with you?
- Play with cause-and-effect toys; talk/sing/read together; respond to baby’s cues.
- Avoid TV, videos, computers; consider making a family media use plan (www.healthychildren. org/MediaUsePlan).
Discipline
◊ Parent expectations with child’s behavior
- Use consistent, positive discipline (limit use of the word no, use distraction, be a role model).
Nutrition and feeding
◊ Self-Feeding
◊ Mealtime Routines
◊ Transition to Solid Foods (table food introduction)
◊ Cup Drinking
◊ Plans for Weaning
- Gradually increase table foods; ensure variety of foods, textures.
- Provide 3 meals and 2 to 3 snacks a day.
- Encourage use of cup; discuss plans for weaning.
- Continue breastfeeding if mutually desired.
Safety
◊ Car Safety Seats
◊ Heatstroke Prevention
◊ Firearm Safety
◊ Safe Home Environment
◊ Burns
◊ Poisoning
◊ Drowning
◊ Falls
- Use rear-facing car safety seat in backseat until child is at least 2 years old
- Never put baby in front seat of vehicle with passenger air bag.
- Use seat belt
- Don’t drive under the influence of alcohol or drugs.
- Avoid heatstroke; never leave baby in car alone.
- Does anyone in your home have a firearm? Have you considered not owning a firearm because of the danger to your child and other family members?
- Remove firearms from home; if firearm necessary, store unloaded and locked, with ammunition locked separately.
- Do home safety check (stair gates, barriers around space heaters, cleaning products, electric cords).
- Don’t leave heavy objects, hot liquids on tablecloths.
- Put Poison Help number (800-222-1222) at each telephone, including cell.
- Use “touch supervision” near water, pools, bathtubs.
- Install operable window guards.
Goals For 9 Month Check up:
- Be gentle and patient
- Get more sleep
- Make a budget
- Leave your work at the office
- Focus on self-care
- Meditate as a family
- Find an outlet
- “cell-free” zone
- Spend more time with your partner
- Take more baths
- Have a girls’/boys’ night
- Be more flexible
- See your child for who they are
- Teach your child to speak up
- Help those less fortunate
- Drink more water
- Find 30 minutes a day of “me” time
- Challenge yourself
- Focus on experiences, not things
- Make health a priority
- Start—or finish—a degree
- Inform yourself
- Maintain balance
- Laugh often
- Cook dinner more frequently
- Ask for help
- Have designated “cheat” days
- Stop having FOMO
- Say “I love you” more often.
- See For Reference ↩︎
- This assessment should be family centered and may include an assessment of child social-emotional health, caregiver depression, and social determinants of health. [Reference] ↩︎
- At each visit, age-appropriate physical examination is essential, with infant totally unclothed and older children undressed and suitably draped. The extent of the physical examination is determined by both the reason for the visit and diagnostic considerations raised during the taking of the history. [Reference] ↩︎
- Blood pressure measurement in infants and children with specific risk conditions should be performed at visits before age 3 years. [Reference] ↩︎
- Instrument-based screening may be used to assess risk at ages 12 and 24 months. [Reference] ↩︎
- For children at risk of lead exposure. [Reference] ↩︎
- Recommend brushing with fluoride toothpaste in the proper dosage for age. [Reference] ↩︎
- Perform a risk assessment. See “Maintaining and Improving the Oral Health of Young Children” (Reference). ↩︎
- Once teeth are present, fluoride varnish may be applied to all children every 3–6 months in the primary care or dental office. (Reference) ↩︎
- If primary water source is deficient in fluoride, consider oral fluoride supplementation. (Reference) ↩︎
- Every visit should be an opportunity to update and complete a child’s immunizations. (Reference) ↩︎