What to except during a 6 Month Old Physical?
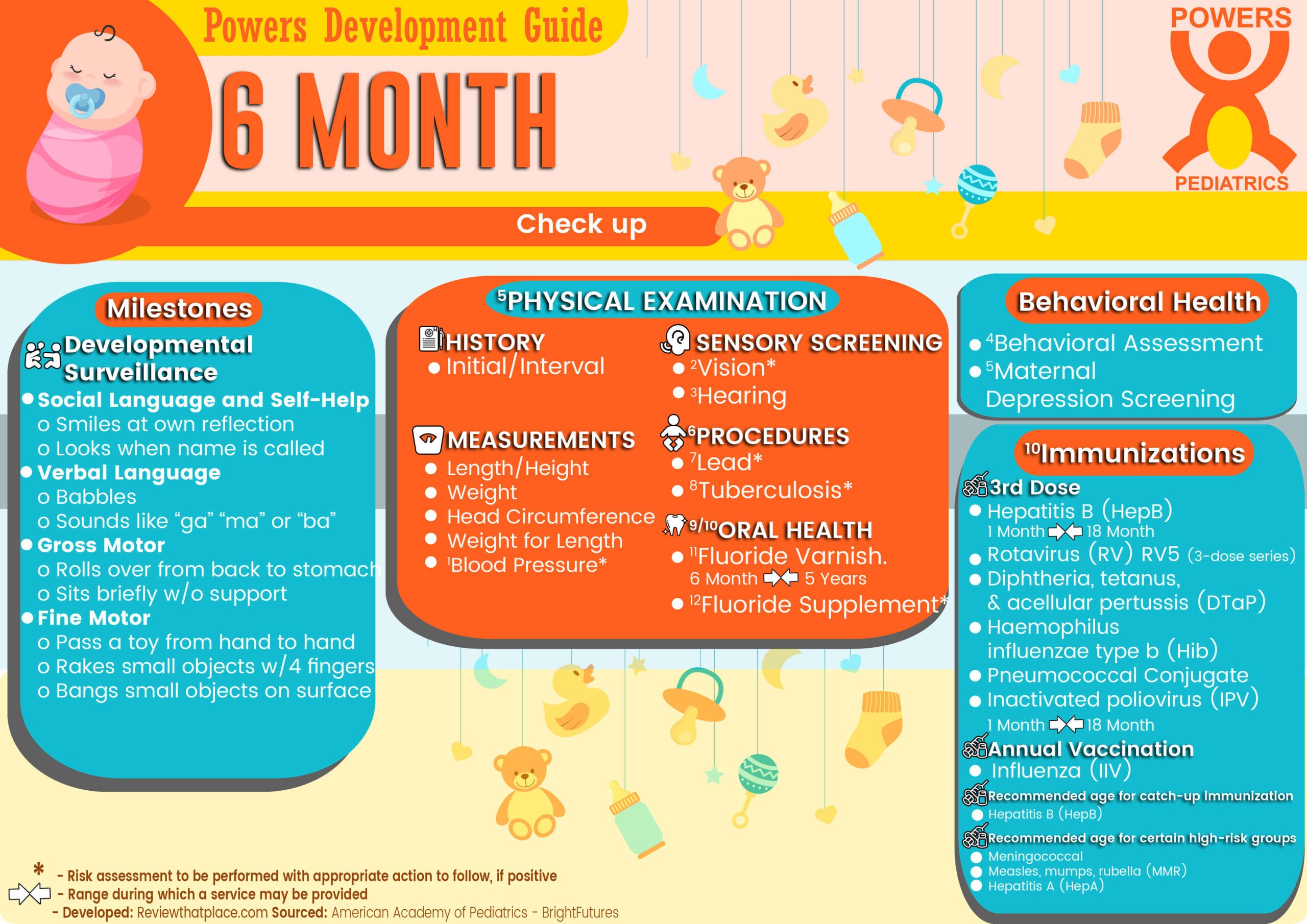
DEVELOPMENTAL SURVEILLANCE
- Social Language and Self-Help
- Smiles at own reflection
- Looks when name is called
- Verbal Language
- Babbles
- Sounds like “ga” “ma” or “ba”
- Gross Motor
- Rolls over from back to stomach
- Sits briefly w/o support
- Fine Motor
- Passes a toy from hand to hand
- Rakes small objects with 4 fingers
- Bangs small objects on surface
BEHAVIOR HEALTH
3 PHYSICAL EXAMINATION
- History
- Initial/Interval
- Measurements
- Length/Height and Weight
- Head Circumference
- Weight for Length
- 4 Blood Pressure*
- Sensory screening
- 5 Vision*
- Hearing*
- 6 7 Oral Health
- Procedures
12 IMMUNIZATION
- Recommended age for certain high-risk groups
- Measles, mumps, rubella (MMR)
- Hepatitis A (HepA)
- Meningococcal (MenACWY-D ≥9 mos; MenACWY-CRM ≥2 mos)
- 3rd Dose Hepatitis B (HepB)
- 1 Month – 9 Month – 12 Month – 15 Month – 18 Month
- 3rd Dose Rotavirus (RV) RV5 (3-dose series)
- 3rd Dose Diphtheria, tetanus, & acellular pertussis (DTaP:<7 yrs)
- 3rd Dose Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib)
- 3rd Dose Pneumococcal conjugate (PCV13)
- 3rd Dose Inactivated poliovirus (IPV: <18 yrs)
- 1 Month – 9 Month – 12 Month – 15 Month – 18 Month
- Influenza (IIV)
- Annual vaccination 1 or 2 doses
range during which a service may be provided
*risk assessment to be performed with appropriate action to follow, if positive
6 Month Old Anticipatory Guidance
Social Determinants of Health
◊ Risks (living situation and food security; tobacco, alcohol, and drugs; parental depression)
◊ Strengths and Protective Factors (family relationships and support, child care)
- Tell me about your living situation. What are your resources for caring for the baby?
- Community agencies can help you with concerns about your living situation.
- Within the past 12 months, were you ever worried whether your food would run out before you got money to buy more? Within the past 12 months, did the food you bought not last and you did not have money to get more?
- Programs like WIC and SNAP are available to help you if you have concerns about your food situation.
- Don’t use tobacco/e-cigarettes/alcohol/drugs.
- Call 800-QUIT-NOW (800-784-8669) for help to quit smoking.
- What are some of your best, and most difficult, times of day with baby? How are you feeling emotionally?
- Ask for help if you feel depressed, overwhelmed.
- Who are you able to go to when you need help with your family?
- Depend on your social network.
- Choose trusted, responsible child care provider.
Infant behavior and development
◊ Parents as Teachers
◊ Communication and Early Literacy
◊ Media ◊ Emerging Infant Independence
◊ Putting Self to Sleep
◊ Self-Calming
- Use high chair /upright seat so baby can see you.
- How does your baby communicate or tell you what he wants and needs?
- Engage in interactive, reciprocal play. Talk/sing/ read to, play games with baby.
- Avoid TV and other digital media with baby.
- Continue regular daily routines; put baby to bed awake but drowsy.
- Continue calming strategies when baby is fussy.
Oral health
◊ Fluoride ◊ Oral Hygiene/Soft Toothbrush ◊ Avoidance of Bottle in Bed
- Assess fluoride source.
- Clean teeth/gums 2 times per day with soft doth/ toothbrush and small smear of fluoridated tooth paste (no more than a grain of rice).
- Don’t prop bottle or use bottle in bed.
- Avoid baby foods / juices that baby sucks out of bag or pouch.
- Don’t share spoons; don’t dean pacifier in your mouth.
Nutrition and feeding
◊ General Guidance on Feeding
◊ Solid Foods ◊ Pesticides in Vegetables and Fruits
◊ Fluids and Juice
◊ Breastfeeding Guidance
◊ Formula Feeding Guidance
- Exclusive breastfeeding for about the first 6 months
- Breast milk and solid foods from about 6 to 12 months
- Iron-fortified formula is recommended substitute.
- Position baby for feeding so you can see/talk to each other.
- Determine whether baby is ready for solids
- Introduce single-ingredient foods one at a time
- Provide iron-rich foods
- Respond to hunger, fullness cues.
- Wash vegetables and fruits before serving; limit juice to 2 to 4 oz per day.
- If breastfeeding:
- Continue as long as mutually desired.
- Continue vitamin D/iron supplementation.
- If formula feeding:
- Don’t switch to milk.
- Contact WIC/community resources for help.
Safety
◊ Car Safety Seats ◊ Safe Sleep ◊ Safe Home Environment ◊ Burns ◊ Sun Exposure ◊ Choking ◊ Poisoning ◊ Drowning ◊ Falls
- Car Seats
- Use rear-facing car safety seat in backseat
- Never put baby in front seat of vehicle with passenger air bag.
- Infants who reach maximum height/weight allowed by their rear-facing-only car safety seat should use a convertible or 3-in- l seat approved for use rear facing to higher weights/heights (up to 50 lb and 49 in).
- Put baby to sleep on back
- Choose crib with slats less than 2¾” apart
- Don’t use loose, soft bedding, lower crib mattress
- Never leave baby in crib with drop side down
- Choose mesh playpen with weave less than ¼
- Do home safety check (stair gates, barriers around space heaters, cleaning products).
- Don’t leave baby alone in tub, high places (changing tables, beds, sofas).
- Keep household products (cleaners, medicines) locked and out of baby’s sight.
- Put Poison Help number (800-222-1222) at all telephones, including cell.
- Keep baby in high chair/playpen when in kitchen.
- Avoid burn risk (drinking hot liquids, cooking, ironing, smoking); set home water temperature less than l 20°F.
- Keep small objects, all plastic bags away from baby.
- To prevent choking, limit finger foods to soft bits.
- Avoid sun exposure; use hat/infant sunscreen
Goals For 6 Month Check up:
- Be gentle and patient
- Get more sleep
- Make a budget
- Leave your work at the office
- Focus on self-care
- Meditate as a family
- Find an outlet
- “cell-free” zone
- Spend more time with your partner
- Take more baths
- Have a girls’/boys’ night
- Be more flexible
- See your child for who they are
- Teach your child to speak up
- Help those less fortunate
- Drink more water
- Find 30 minutes a day of “me” time
- Challenge yourself
- Focus on experiences, not things
- Make health a priority
- Start—or finish—a degree
- Inform yourself
- Maintain balance
- Laugh often
- Cook dinner more frequently
- Ask for help
- Have designated “cheat” days
- Stop having FOMO
- Say “I love you” more often.
- This assessment should be family centered and may include an assessment of child social-emotional health, caregiver depression, and social determinants of health. [Reference] ↩︎
- Screening should occur per. [Reference] ↩︎
- At each visit, age-appropriate physical examination is essential, with infant totally unclothed and older children undressed and suitably draped. The extent of the physical examination is determined by both the reason for the visit and diagnostic considerations raised during the taking of the history.[Reference] ↩︎
- Blood pressure measurement in infants and children with specific risk conditions should be performed at visits before age 3 years. [Reference] ↩︎
- Instrument-based screening may be used to assess risk at ages 12 and 24 months. [Reference] ↩︎
- Recommend brushing with fluoride toothpaste in the proper dosage for age. [Reference] ↩︎
- Perform a risk assessment. ↩︎
- Once teeth are present, fluoride varnish may be applied to all children every 3–6 months in the primary care or dental office. [Reference] ↩︎
- If primary water source is deficient in fluoride, consider oral fluoride supplementation. [Reference] ↩︎
- For children at risk of lead exposure. [Reference] ↩︎
- Testing should be performed on recognition of high-risk factors. Tuberculosis testing per recommendations of the AAP Committee on Infectious Diseases. ↩︎
- Every visit should be an opportunity to update and complete a child’s immunizations.[Reference] ↩︎