What to except during a 3 to 5 Day Old Physical?
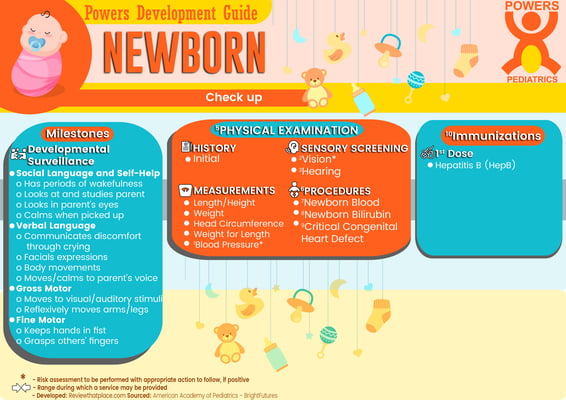
Developmental Surveillance
- Social Language and Self-Help
- Periods of Wakefulness for feeding
- Verbal Language
- Cries with discomfort
- Calms to adult voice
- Gross Motor
- Lifts head briefly
- Turns to the side
- Reflexively moves arms and legs
- Fine Motor
- Keeps hands in a fist
PHYSICAL EXAMINATION
- History
- Initial/Interval
- Measurements
- Length/Height and Weight
- Head Circumference
- Weight for Length
- Blood Pressure
- PROCEDURES
- Newborn Blood
- Range during which a service may be provided: 3-5 days – 1 Month – 2 Month
- Newborn Bilirubin
- Critical Congenital Heart Defect
- SENSORY SCREENING
- Vision
- Hearing
- Range during which a service may be provided: 3-5 days – 1 Month – 2 Month
Immunization
- Not Required
- Blood pressure measurement in infants and children with specific risk conditions should be performed at visits before age 3 years. [Reference]
- Instrument-based screening may be used to assess risk at ages 12 and 24 months.[Reference]
- Verify results as soon as possible, and follow up, as appropriate.
- This assessment should be family centered and may include an assessment of child social-emotional health, caregiver depression, and social determinants of health.[Reference]
- At each visit, age-appropriate physical examination is essential, with infant totally unclothed and older children undressed and suitably draped. The extent of the physical examination is determined by both the reason for the visit and diagnostic considerations raised during the taking of the history. [Reference]).
- Every visit should be an opportunity to update and complete a child’s immunizations.[Reference]
3 to 5 Days Old Anticipatory Guidance
Social Determinants of Health
◊Risks (living situation and food security, environmental tobacco exposure, intimate partner violence, maternal alcohol and substance use) ◊
Strengths and protective factors (family support, parent newborn relationship)
- Tell me about your living situation. What are your resources for caring for the baby?
- Community agencies can help you with concerns about your living situation.
- Within the past 12 months, were you ever worried whether your food would run out before you got money to buy more? Within the past 12 months, did the food you bought not last and you did not have money to get more?
- Programs like WIC and SNAP are available to help you if you have concerns about your food situation.
- Don’t use tobacco/e-cigarettes. Keep car/home free of tobacco smoke/e-cigarette vapor.
- Call 800-QUIT-NOW (800-784-8669) for help to quit smoking.
- Reach out to and accept help from family and friends.
Parent and family health and well-being
◊ Transition Home ◊ Sibling Adjustment
- Ask for help from family or friends.
- Rest and sleep when baby sleeps.
- Spend time with your other children; maintain family routines to help them adjust to baby.
Newborn behavior and care
◊ Early Brain Development ◊ Adjustment to Home ◊ Calming ◊ When to Call (temperature taking) ◊ Emergency Readiness (CPR) ◊ Illness Prevention (handwashing, outings) ◊ Sun Exposure
- Sing/talk/read to baby; avoid TV and other digital media.
- Help baby wake for feeding by patting/diaper change/undressing.
- Calm baby with stroking head or gentle rocking.
- What do you do to calm your baby? What do you do if that doesn’t work?
- Never hit or shake baby.
- What type of thermometer do you have? Do you know how to use it?
- Take temperature rectally, not by ear or skin.
- Create emergency preparedness plan (first aid kit, list of telephone numbers).
- Wash hands often; avoid crowds.
- Avoid sun; use infant sunscreen.
Nutrition and feeding
◊ General Guidance on Feeding (weight gain, feeding strategies, holding, burping, hunger and satiation cues)
◊ Breastfeeding Guidance
◊ Formula-feeding Guidance
- How do you know if your baby is hungry? How do you know if your baby has had enough to eat?
- Exclusive breastfeeding for about the first 6 months provides ideal nutrition
- Supports best growth and development
- Iron-fortified formula is recommended substitute
- Recognize signs of hunger, fullness
- Develop feeding routine
- Adequate weight gain is 6 to 8 wet cloth diapers per day or 5 to 6 wet disposable diapers, 3 to 4 stools per day; give no extra fluids.
- If breastfeeding: How is breastfeeding going? What concerns do you have about breastfeeding?
- Feed every 1 to 3 hours daytime
- Every 3 hours nighttime for 8 to 12 feedings in 24 hours
- Begin giving baby vitamin D (400 IU per day)
- Mothers should continue prenatal vitamin with iron; eat a healthy diet (vegetables /fruit /whole grains/low-fat or nonfat dairy/fish/lean protein).
- If formula feeding:
- Prepare/store formula safely
- Feed 2 oz every 2 to 3 hours, more if still seems hungry
- Hold baby semi-upright; don’t prop bottle.
Safety
◊ Car Safety Seats ◊ Heatstroke Prevention ◊ Safe Sleep ◊ Pets ◊ Safe Home Environment
- Car Seat
- Use rear-facing car safety seat in backseat
- Never put baby in front seat of vehicle with passenger air bag
- Keep baby in car safety seat at all times during travel.
- Always use seat belt; do not drive under the influence of alcohol or drugs.
- Prevent heatstroke; never leave your baby alone in a car.
- Put baby to sleep on back; choose crib with slats less than 2 ¾ apart; don’t use loose, soft bedding; have baby sleep in your room in own crib.
- Don’t drink hot liquids while holding baby; set home water temperature less than 120°F
Goals For 3-5 day Check up:
- Be gentle and patient
- Get more sleep
- Make a budget
- Leave your work at the office
- Focus on self-care
- Meditate as a family
- Find an outlet
- “cell-free” zone
- Spend more time with your partner
- Take more baths
- Have a girls’/boys’ night
- Be more flexible
- See your child for who they are
- Teach your child to speak up
- Help those less fortunate
- Drink more water
- Find 30 minutes a day of “me” time
- Challenge yourself
- Focus on experiences, not things
- Make health a priority
- Start—or finish—a degree
- Inform yourself
- Maintain balance
- Laugh often
- Cook dinner more frequently
- Ask for help
- Have designated “cheat” days
- Stop having FOMO
- Say “I love you” more often.