What to except during a 9 Month Old Physical
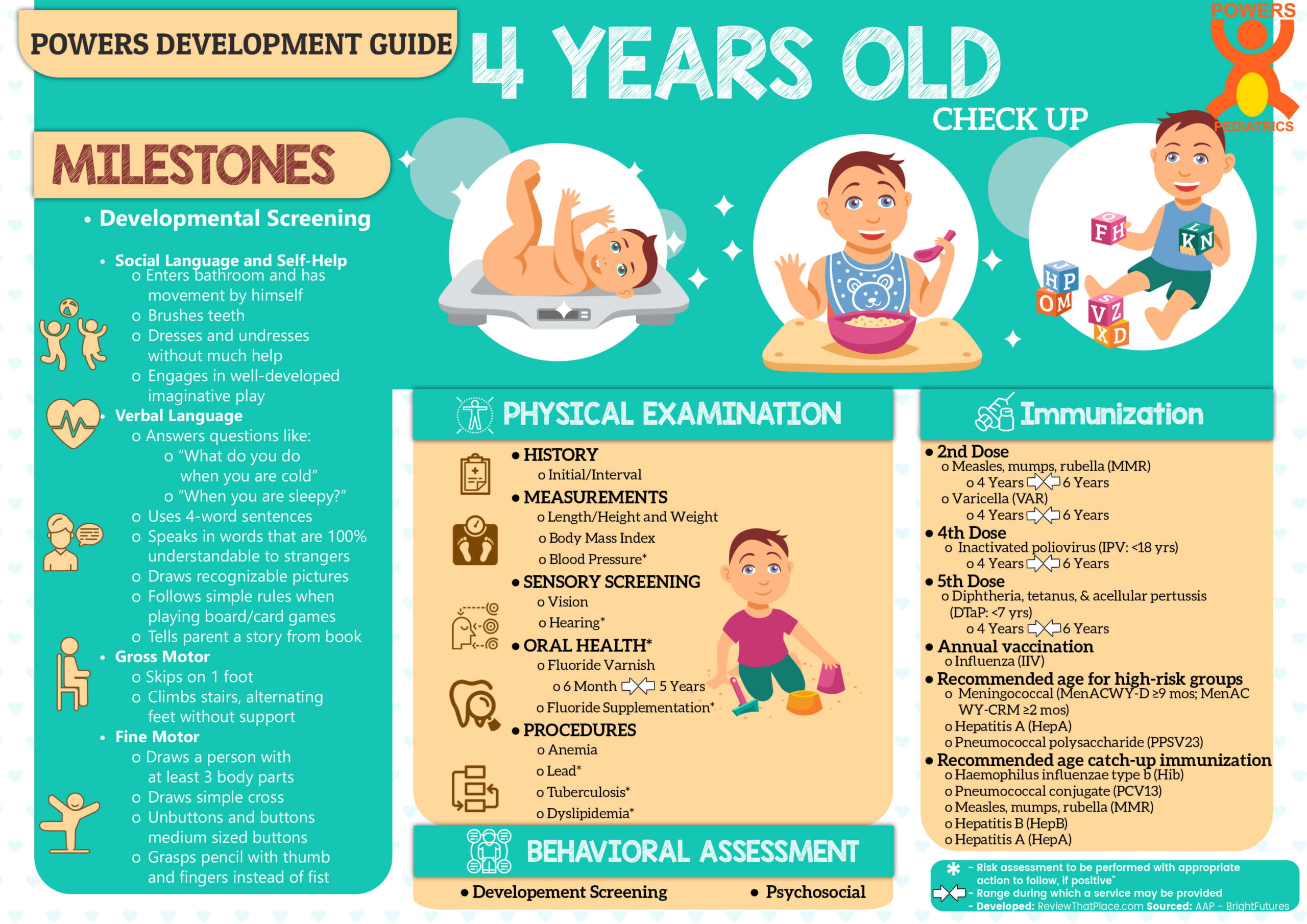
1 DEVELOPMENTAL SCREENING
- Social Language and Self-Help
- Enters bathroom and has movement by himself
- Brushes teeth
- Dresses and undresses without much help
- Engages in well-developed imaginative play
- Verbal Language
- Answers questions like:
- “What do you do when you are cold”
- “When you are sleepy?”
- Uses 4-word sentences
- Speaks in words that are 100% understandable to strangers
- Draws recognizable pictures
- Follows simple rules when playing board/card games
- Tells parent a story from book
- Gross Motor
- Skips on 1 foot
- Climbs stairs, alternating feet without support
- Fine Motor
- Draws a person with at least 3 body parts
- Draws simple cross
- Unbuttons and buttons medium sized buttons
- Grasps pencil with thumb and fingers instead of fist
BEHAVIORAL HEALTH
- Developmental Surveillance
- 2 Psychosocial/Behavioral Assessment
3 PHYSICAL EXAMINATION
15 Immunization
- 2nd Dose
- Measles, mumps, rubella (MMR)
- 4 Years 6 Years
- Varicella (VAR)
- 4 Years 6 Years
- 4th Dose
- Inactivated poliovirus (IPV: <18 yrs)
- 4 Years 6 Years
- 5th Dose
- Diphtheria, tetanus, & acellular pertussis (DTaP: <7 yrs)
- 4 Years 6 Years
- Annual vaccination
- Influenza (IIV)
- Recommended age for certain high-risk groups
- Meningococcal (MenACWY-D ≥9 mos; MenACWY-CRM ≥2 mos)
- Hepatitis A (HepA)
- Pneumococcal polysaccharide (PPSV23)
- Recommended age for catch-up immunization
- Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib)
- Pneumococcal conjugate (PCV13)
- Hepatitis B (HepB)
- Hepatitis A (HepA)
4 Years Old Anticipatory Guidance
Social determinants of health
◊ Risks (living situation and food security; tobacco, alcohol, and drugs; intimate partner violence; safety in the community)
◊ Strengths and Protective Factors (engagement in the community)
- Tell me about your living situation. Do you have the things you need to care for your child?
- Community agencies can help you with concerns about your living situation.
- Within the past 12 months, were you ever worried whether your food would run out before you got money to buy more? Within the past 12 months, did the food you bought not last and you did not have money to get more?
- Programs like WIC and SNAP are available to help you if you have concerns about your food situation.
- Don’t use tobacco /e-cigarettes/alcohol/drugs. Call 800-QUIT-NOW (800-784-8669) for help to quit smoking.
- Do you always feel safe in your home? Has your partner ever hit, kicked, or shoved you, or physically hurt you or your child? Would you like information on where to go or who to contact if you ever need help?
- Ask for help if you are concerned about or have experienced violence from your partner or another significant person in your life.
- You can also call the National Domestic Violence Hotline toll-free at 800-799-SAFE (7233).
- Teach your child rules for how to be safe with adults: (1) no adult should tell a child to keep secrets from parents; (2) no adult should express interest in private parts; (3) no adult should ask a child for help with his/ her private parts.
- What activities do you participate in outside the home? What help do you need in finding other community resources, such as a faith-based group, recreational centers, or volunteer opportunities?
- Maintain or expand participation in community activities.
School readiness
◊ Language Understanding and Fluency
◊ Feelings
◊ Opportunities to Socialize with Other Children
◊ Readiness for Structured Learning Experiences
◊ Early Childhood Programs and Preschool
- How does your child communicate what she wants and knows?
- Give child time to finish sentences; encourage speaking skills by reading/talking together. Keep answers short and simple.
- Read together daily; ask child questions about the stories.
- Children are very sensitive, either easily encouraged or hurt; model respectful behavior and apologize if wrong; praise when demonstrates sensitivity to feelings of others.
- How interested is your child in other children? How confident is she socially and emotionally?
- Provide opportunities for your child to play with other children.
- How happy are you with your preschool or child care arrangements? On most days, does she seem happy to go?
- Visit your child’s preschool/child care program; become actively involved; talk with your child about what she’s learning.
Developing healthy nutrition and personal habits
◊ Water ◊ Milk and Juice ◊ Nutritious Foods
◊ Daily Routines that Promote Health Always have cool water available.
- Provide 16 to 24 oz low-fat /fat- free milk daily.
- Juice is not a necessary drink. If you choose to give juice, limit to 4 oz daily and always serve it with a meal.
- Offer variety of healthy foods/snacks, especially vegetables, fruits, lean protein.
- Trust child to decide how much to eat.
- Create calm bedtime ritual; enjoy mealtimes without TV; ensure child brushes teeth twice a day with pea-sized fluoridated toothpaste.
Media use
◊ Limits on Use
◊ Promoting Physical Activity and Safe Play
- What digital and Internet-connected devices does your child use (eg, handheld devices, video games, digital toys, TV, computers)?
- Limit TV and video to no more than 1 hour a day; no TV in bedroom; supervise any Internet use; consider making a family media use plan (www.healthychildren.org/MediaUsePlan).
- Make opportunities for daily play; be physically active as a family.
Safety
◊ Belt-Positioning Car Booster Seats
◊ Outdoor Safety ◊ Water Safety
◊ Sun Protection ◊ Pets ◊ Firearm Safety
- Where do you sit when you ride in the car? Do you have a special seat?
- Continue to use a size-appropriate forward facing car safety seat installed in backseat.
- Supervise all outdoor play; never leave child alone; don’t allow to cross street alone.
- Be sure swimming pools are fenced; use life jacket; teach child to swim.
- Use hat/sun protection clothing, sunscreen; avoid prolonged exposure when sun is strongest, between 11:00 am and 3:00 pm.
- Teach child about safety around pets.
- Remove firearms from home; if firearm necessary, store unloaded and locked, with ammunition locked separately. Ask if firearms in other homes where child plays; if so, ensure same safety precautions before letting child play there.
Goals For 4 Year Check up:
- Be gentle and patient
- Get more sleep
- Make a budget
- Leave your work at the office
- Focus on self-care
- Meditate as a family
- Find an outlet
- “cell-free” zone
- Spend more time with your partner
- Take more baths
- Have a girls’/boys’ night
- Be more flexible
- See your child for who they are
- Teach your child to speak up
- Help those less fortunate
- Drink more water
- Find 30 minutes a day of “me” time
- Challenge yourself
- Focus on experiences, not things
- Make health a priority
- Start—or finish—a degree
- Inform yourself
- Maintain balance
- Laugh often
- Cook dinner more frequently
- Ask for help
- Have designated “cheat” days
- Stop having FOMO
- Say “I love you” more often
- A visual acuity screen is recommended at ages 4 and 5 years, as well as in cooperative 3-year-olds. Instrument-based screening may be used to assess risk at ages 12 and 24 months, in addition to the well visits at 3 through 5 years of age. (Reference) ↩︎
- This assessment should be family centered and may include an assessment of child social-emotional health, caregiver depression, and social determinants of health. (Reference) ↩︎
- At each visit, age-appropriate physical examination is essential, with infant totally unclothed and older children undressed and suitably draped. The extent of the physical examination is determined by both the reason for the visit and diagnostic considerations raised during the taking of the history. (Reference) ↩︎
- Screen, per reference. ↩︎
- Blood pressure measurement in infants and children with specific risk conditions should be performed at visits before age 3 years. (Reference) ↩︎
- A visual acuity screen is recommended at ages 4 and 5 years, as well as in cooperative 3-year-olds. Instrument-based screening may be used to assess risk at ages 12 and 24 months, in addition to the well visits at 3 through 5 years of age. (Reference) ↩︎
- Recommend brushing with fluoride toothpaste in the proper dosage for age. (Reference) ↩︎
- Once teeth are present, fluoride varnish may be applied to all children every 3–6 months in the primary care or dental office. (Reference) ↩︎
- If primary water source is deficient in fluoride, consider oral fluoride supplementation. (Reference) ↩︎
- These may be modified, depending on entry point into schedule and individual need. ↩︎
- Perform risk assessment or screening, as appropriate, per recommendations in the current edition of the AAP Pediatric Nutrition: Policy of the American Academy of Pediatrics (Iron chapter). ↩︎
- For children at risk of lead exposure, see per reference. ↩︎
- Testing should be performed on recognition of high-risk factors. Tuberculosis testing per recommendations of the AAP Committee on Infectious Diseases. ↩︎
- See per reference. ↩︎
- Every visit should be an opportunity to update and complete a child’s immunizations. (Reference) ↩︎