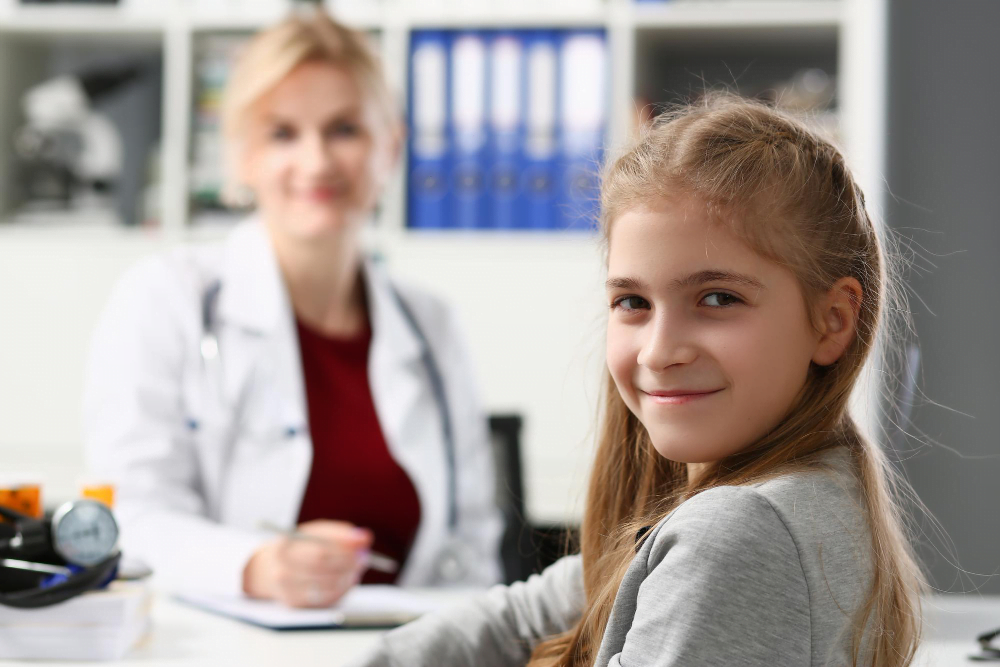
The journey from pediatric care to adult healthcare can be confusing for many. This guide aims to simplify the transition process, ensuring you know when to stop going to a pediatrician and switch to an adult doctor.
You’ll learn the ideal age to transition, key considerations, and tips to make the change seamless. Rest assured, the topic isn’t complex, and you can grasp it easily.
Understanding Pediatric Care
Understanding pediatric care is vital in determining when to transition to an adult doctor. Pediatricians are specialists trained in managing the health of infants, children, and adolescents.
Pediatric care focuses on:
- Growth and Development: Monitoring developmental milestones.
- Preventive Care: Vaccinations and routine check-ups.
- Health Education: Informing parents and young patients about healthy habits.
- Chronic Conditions: Managing illnesses and conditions specific to children, like asthma and cystic fibrosis.
Most pediatricians offer services from birth up to a set age, typically 18-21, although this age limit may vary. Understanding these parameters can help in knowing when to transition your young adult to a family medicine physician or another adult doctor.
What is the age range for pediatric patients?
The age range for pediatric patients typically spans from birth up to 18 years, though some practices extend care to 21 years.
- Infants: Birth to 1 year.
- Children: 1 year to 12 years.
- Adolescents: 13 years to 18-21 years.
During adolescence, pediatricians address unique needs that include physical growth, emotional changes, and the onset of puberty. Pediatricians are specially trained to handle these developmental stages.
However, once young adults reach the latter part of adolescence, it may become practical to consider transitioning to a doctor experienced in adult medicine.
Should a 17-year-old still go to a pediatrician?
The appropriateness of a 17-year-old continuing pediatric care depends on individual health needs and comfort levels. Pediatricians specialize in adolescent medicine, making them adept at:
- Mental Health: Addressing issues like anxiety, depression, and social pressures.
- Sexual Health: Providing guidance on safe practices and managing related health issues.
- Growth and Development: Ensuring milestone achievements align with age norms.
However, reasons to consider a switch include:
- Preparation for Adult Medicine: Preparing them for managing their health.
- Complex Health Needs: Conditions better managed by adult specialists, like high cholesterol or neurological conditions.
In many cases, a gradual transition can provide adequate support while easing the patient into adult healthcare systems.
What is the oldest age to go to a pediatrician?
The oldest age to go to a pediatrician generally falls between 18 and 21 years. This age limit can vary based on:
- Pediatric Medical Practice Policies: Policies differ; some pediatricians may see patients until they complete their college years.
- Health Needs: Complex pediatric-specific conditions, such as sickle cell disease or cystic fibrosis, might necessitate extended pediatric care.
- Patient Comfort Levels: Adolescents accustomed to their pediatricians might take more time to feel comfortable transitioning.
Nonetheless, transitioning by age 21 helps ensure they are integrated into adult care systems, which becomes crucial for long-term health management.
When to Transition to an Adult Doctor
Knowing when to transition to an adult doctor is crucial. This decision typically hinges on various signs and factors indicating readiness for adult care.
Signs It’s Time to Switch
Look for these signs to determine if it’s time:
- Age Milestones: Approaching the upper pediatric age limit, typically 18-21.
- Independence: Gaining independence and responsibility for personal health.
- Complex Health Issues: Managing adult-specific health concerns.
Factors to Consider
Several factors influence the decision to switch doctors:
- Health Conditions: Are they more complex and need adult specialists?
- Lifestyle Changes: Entering college or starting a job, affects accessibility.
- Comfort Levels: Whether they feel comfortable with a new healthcare environment.
Considering these factors ensures a smooth transition from pediatric to adult care, accommodating individualized health needs effectively.
Choosing the Right Adult Doctor
Selecting the right adult doctor is pivotal for seamless healthcare continuity. The goal is to find a healthcare provider specialized in managing adult health issues.
Differences Between Pediatricians and Family Medicine Physicians
Understanding the differences between pediatricians and family medicine physicians or internal medicine physicians helps in making an informed choice.
Role of a Family Medicine Physician
A family medicine physician is specially trained to provide healthcare for patients of all ages, making them a versatile choice for transitioning from pediatric care:
- Continuity of Care: They manage health from childhood through adulthood.
- Whole-Family Care: They can treat various family members, ensuring comprehensive care.
- Preventive Services: Focus on long-term health monitoring and preventive care.
Benefits of Staying with the Same Doctor
Staying with the same family medicine physician throughout life’s stages offers several benefits:
- Medical History Insight: Continuity helps maintain comprehensive medical records.
- Comfort and Trust: Builds a more trusted patient-doctor relationship.
- Holistic Health Management: A better understanding of family health history influences personalized care plans.
Understanding these roles and benefits aids in deciding which healthcare provider best fits your needs.
How to Make the Transition Smooth
Making a smooth transition from pediatric to adult care involves thoughtful steps and preparation.
Communicating with Your Pediatrician
Effective communication with your pediatrician about the transition is essential:
- Discuss Timing: Plan discussions around key age milestones or life changes.
- Get Recommendations: Request referrals to trusted adult care providers.
- Health Transition Plan: Develop a comprehensive plan outlining the transitioning period.
Preparing Your Medical Records
Ensuring your medical records transfer securely is crucial for continuity:
- Request Copies: Obtain copies or summaries of your medical records.
- Update Information: Ensure all health conditions and treatments are current.
- Transfer Documents: Work with both healthcare providers to securely transfer records.
Building a Relationship with Your New Doctor
Developing a trusted relationship with your new doctor enhances healthcare experiences:
- Initial Appointments: Use the first visits to discuss health history and expectations.
- Open Communication: Maintain transparent communication for a better understanding of health needs.
- Understand Their Approach: Learn about their care style and procedures to align expectations.
Final Thoughts
Transitioning from a pediatrician to an adult doctor is a significant change but manageable with the right approach. Embrace this journey and ensure your healthcare needs evolve with you, providing a solid foundation for long-term well-being. For further resources, consult your current healthcare providers or refer to specialist clinics accessible within your community.