What to except during a 7 Year Old Physical?
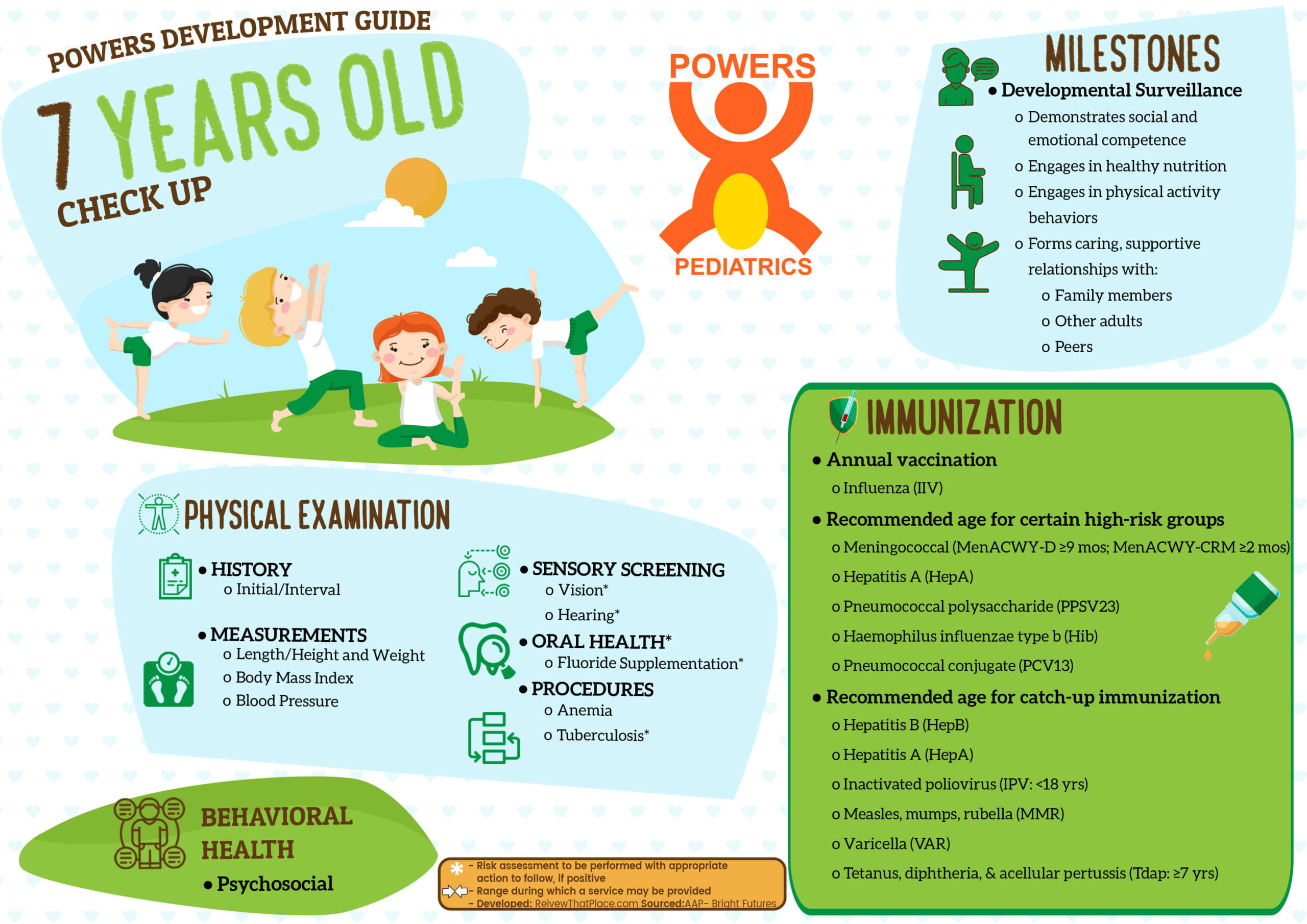
DEVELOPMENTAL SURVEILLANCE
- Demonstrates social and emotional competence
- Engages in healthy nutrition
- Engages in physical activity behaviors
- Forms caring, supportive relationships with:
- Family members
- Other adults
- Peers
BEHAVIORAL HEALTH
- 1 Psychosocial/Behavioral Assessment
2 PHYSICAL EXAMINATION
- History
- Initial/Interval
- Measurements
- Sensory Screening
- 5 Vision*
- Hearing*
- Oral Health
- 6 Fluoride Supplementation*
- 7 Procedures
10 IMMUNIZATION
- Recommended age for certain high-risk groups
- Meningococcal (MenACWY-D ≥9 mos; MenACWY-CRM ≥2 mos)
- Hepatitis A (HepA)
- Pneumococcal polysaccharide (PPSV23)
- Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib)
- Pneumococcal conjugate (PCV13)
- Recommended age for catch-up immunization
- Hepatitis B (HepB)
- Hepatitis A (HepA)
- Inactivated poliovirus (IPV: <18 yrs)
- Measles, mumps, rubella (MMR)
- Varicella (VAR)
- Tetanus, diphtheria, & acellular pertussis (Tdap: ≥7 yrs)
- Influenza (IIV)
- Annual vaccination 1 or 2 doses
7 Year Old Anticipatory Guidance
Social determinants of health
◊ Risks (neighborhood and family violence, food security, family substance use, harm from the Internet) ◊ Strengths and Protective Factors (emotional security and self-esteem, connectedness with family and peers)
- Teach your child nonviolent conflict-resolution techniques.
- Talk with parents/trusted adult if you are bullied.
- Within the past 12 months, were you ever worried whether your food would run out before you got money to buy more? Within the past 12 months, did the food you bought not last and you did not have money to get more?
- Contact community resources, like SNAP, for help with food assistance.
- Don’t use tobacco/e-cigarettes.
- Call 800-QUIT NOW (800-784-8669) for help to quit smoking. Talk with me if you are worried about family member drug/alcohol use.
- How much do you know about your child’s Internet use?
- Put family computer in easily seen place; monitor computer use; ins tall safety filter.
- What would you do if you went on a site that scared you?
- Don’t give out personal information online.
- Encourage independence, self-responsibility; show affection; praise appropriately.
- How are you getting along as a family? What do you do together?
- Spend time with your child. Make time to talk. Know child’s friends.
Development and mental health
◊ Independence ◊ Rules and Consequences ◊ Temper Problems
◊ Conflict Resolution ◊ Puberty and Pubertal Development Encourage competence/independence / self-responsibility.
- Discuss rules, consequences.
- Who do you talk with about your worries and things that make you mad?
- Be positive role model; do not hit or let others hit.
- Talk about worries.
- What have you told your child about how to care for his changing body? Do you know what puberty is? Has anyone talked with you about how your body will change during puberty?
- Be aware of pubertal changes; answer questions simply.
School
◊ Adaptation to School ◊ School Problems (behavior or learning issues)
◊ School Performance and Progress
◊ School Attendance
◊ IEP or Special Education Services
◊ Involvement in School Activities
◊ After-School Programs
◊ Parental Involvement Ensure child is ready to learn (regular bedtime routine, healthy breakfast).
- How is your child doing in school? What types of activities is your child doing after school? What do you like best about school/after school activities?
- Show interest in school and activities.
- If concerns, ask teacher about evaluation for special help/tutoring; help with bullying.
- If child has special health care needs, be active in IEP process.
Physical growth and development
◊ Oral health (regular visits with dentist, daily brushing and flossing, adequate fluoride, avoidance of sugar sweetened beverages and snacks)
◊ Nutrition (healthy weight, adequate calcium and vitamin D intake, limiting added sugars intake)
◊ Physical Activity (60 minutes of physical activity a day, screen time)
- Take child to dentist twice a year.
- Give fluoride supplement if dentist recommends.
- Limit sweetened drinks /snacks.
- Brush teeth twice a day; floss once.
- Wear mouth guard during sports.
- Help child choose healthy eating (provide healthy foods, eat together as a family, be a role model) .
- Eat breakfast; eat vegetables/fruits.
- Eat when you’re hungry; stop when you’re satisfied.
- Drink milk 3 or more times a day.
- Limit sugary drinks/foods.
- Be physically active often during the day.
- Consider making family media use plan (www. healthychildren.org/MediaUsePlan), which can help balance child’s needs for physical activity, sleep, school activities, and unplugged time; decide on rules for media time in time left over after all other activities; take into account quantity, quality, location of media use.
Safety
◊ Car Safety
◊ Safety During Physical Activity
◊ Water Safety ◊ Sun Protection
◊ Harm From Adults
◊ Firearm Safety Use belt-positioning booster seat in backseat.
- Ensure child uses safety equipment (helmet, pads). Be a role model and always wear a helmet.
- Teach child to swim; supervise around water.
- Use sunscreen; wear hat; avoid prolonged exposure when sun is strongest, between 11:00 am and 3:00 pm.
- Do you know what do you if you get home and Mom or Dad is not there? What would you do if you felt unsafe at a friend’s house? Has anyone touched you in a way that made you feel uncomfortable?
- Know child’s friends; teach home safety rules for fire /emergencies; teach rules for how to be safe with adults:
- (1) no adult should tell a child to keep secrets from parents; (2) no adult should express interest in private parts; (3) no adult should ask a child for help with his/her private parts.
- Remove firearms from home; if firearm necessary, store unloaded and locked, with ammunition locked separately.
Goals For 7 Year Check up:
- Be gentle and patient
- Get more sleep
- Make a budget
- Leave your work at the office
- Focus on self-care ◌ Meditate as a family
- Find an outlet
- “cell-free” zone
- Spend more time with your partner
- Take more baths
- Have a girls’/boys’ night
- Be more flexible
- See your child for who they are
- Teach your child to speak up
- Help those less fortunate
- Drink more water
- Find 30 minutes a day of “me” time
- Challenge yourself
- Focus on experiences, not things
- Make health a priority
- Start—or finish—a degree
- Inform yourself
- Maintain balance
- Laugh often
- Cook dinner more frequently
- Ask for help
- Have designated “cheat” days
- Stop having FOMO
- Say “I love you” more often
- This assessment should be family centered and may include an assessment of child social-emotional health, caregiver depression, and social determinants of health. (Reference) ↩︎
- At each visit, age-appropriate physical examination is essential, with infant totally unclothed and older children undressed and suitably draped. The extent of the physical examination is determined by both the reason for the visit and diagnostic considerations raised during the taking of the history. (Reference) ↩︎
- Screen, per reference ↩︎
- Blood pressure measurement in infants and children with specific risk conditions should be performed at visits before age 3 years. (Reference). ↩︎
- A visual acuity screen is recommended at ages 4 and 5 years, as well as in cooperative 3-year-olds. Instrument-based screening may be used to assess risk at ages 12 and 24 months, in addition to the well visits at 3 through 5 years of age. (Reference) ↩︎
- If primary water source is deficient in fluoride, consider oral fluoride supplementation. (Reference) ↩︎
- These may be modified, depending on entry point into schedule and individual need. ↩︎
- Perform risk assessment or screening, as appropriate, per recommendations in the current edition of the AAP Pediatric Nutrition: Policy of the American Academy of Pediatrics (Iron chapter). ↩︎
- Testing should be performed on recognition of high-risk factors. Tuberculosis testing per recommendations of the AAP Committee on Infectious Diseases. ↩︎
- Every visit should be an opportunity to update and complete a child’s immunizations. (Reference) ↩︎